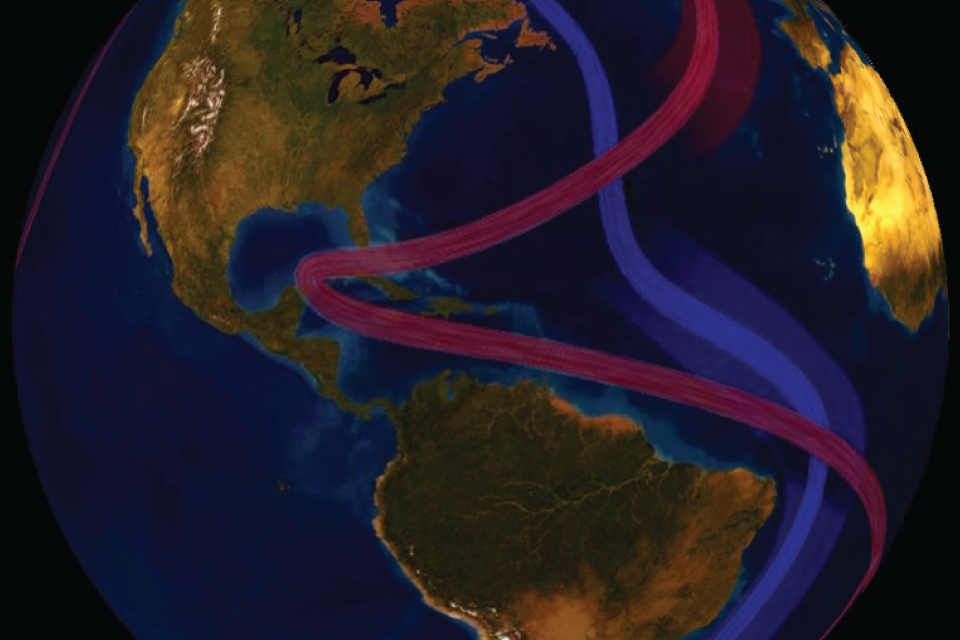
The ocean’s water is constantly circulated by currents. Tidal currents occur close to shore and are influenced by the sun and moon. Surface currents are influenced by the wind. However, other, much slower currents that occur from the surface to the seafloor are driven by changes in the saltiness and ocean temperature, a process called thermohaline circulation. These currents are carried in a large “global conveyor belt,” which includes the AMOC.
AMOC stands for Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. The AMOC circulates water from north to south and back in a long cycle within the Atlantic Ocean. This circulation brings warmth to various parts of the globe and also carries nutrients necessary to sustain ocean life.